What concerns booksellers, publishers and readers most is the tariffs on children's book, even though they are delayed until mid-December. Independent bookstores, often with tight profit margins, might have to suffer financially, and children, in the more pessimistic scenario, could have fewer books to read.
CHAPEL HILL, the United States, Sept. 5 (Xinhua) -- Jamie Fiocco, owner of Flyleaf Books, a bookstore in the U.S. state of North Carolina, said that she has been running the bookstore for 10 years and every year has been the best ever. But she could only hope for the best this year.
It's "disappointing" that books, which were traditionally exempted from tariffs, are included in the U.S. government's new tariff list of Chinese imports, said Fiocco, who is also the president of the American Booksellers Association, which represents some 2,000 independent brick-and-mortar booksellers across the country.
What concerns booksellers, publishers and readers most is the tariffs on children's book, even though they are delayed until mid-December. Independent bookstores, often with tight profit margins, might have to suffer financially, and children, in the more pessimistic scenario, could have fewer books to read.
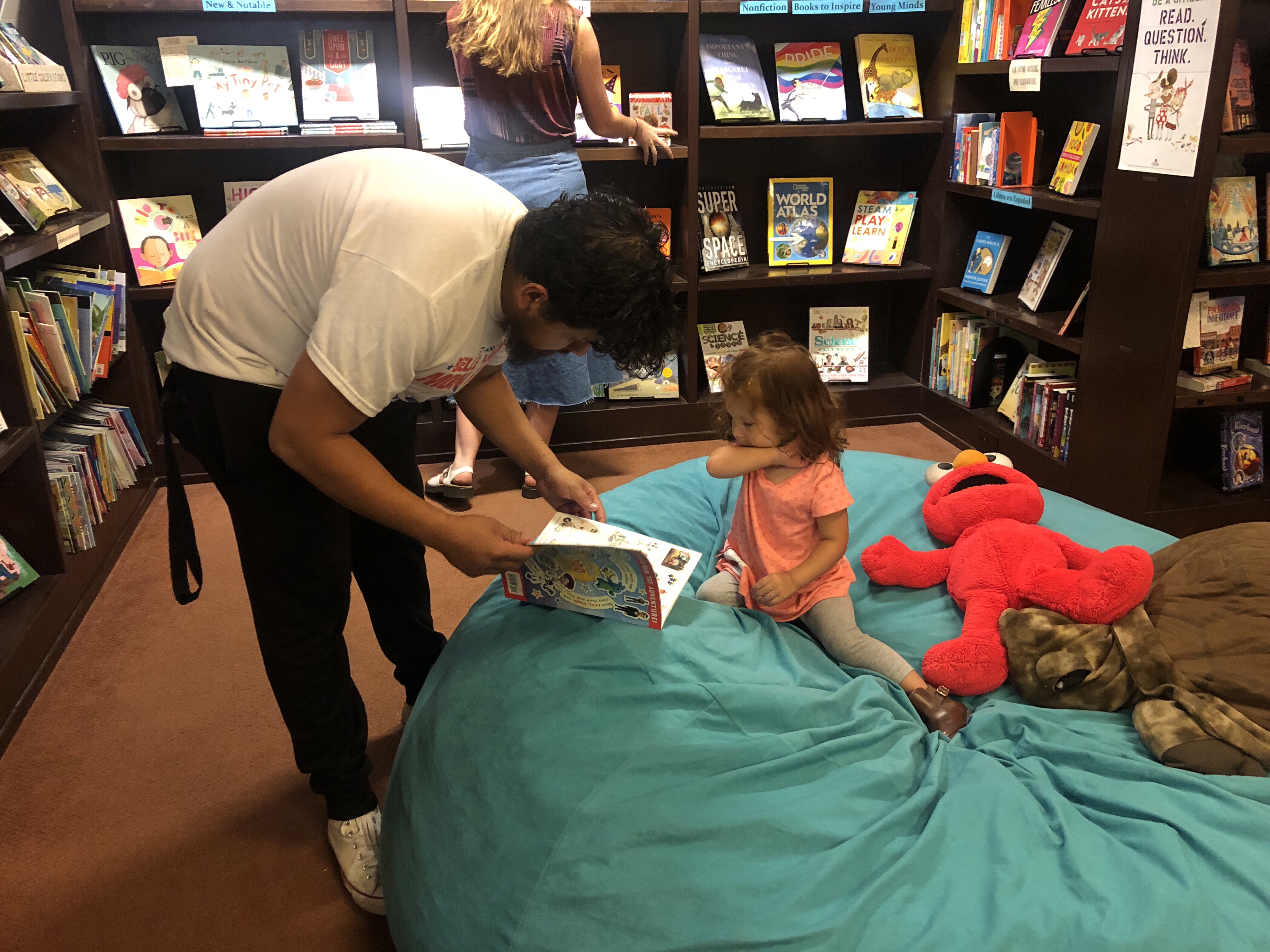
Photo taken with mobile phone shows a man reading to a girl at the Flyleaf Books bookstore in Chapel Hill in the North Carolina, the United States, Aug 27, 2019. (Xinhua/Xiong Maoling)
LARGELY PRINTED IN CHINA
Fiocco's 15-person bookstore is located in Chapel Hill, North Carolina, with a vibrant, diverse children's book section. A blue bean bag sofa with a few toys makes it attractive for kids, who would sit comfortably with their parents to read books.
Randomly checking out a dozen children's books would lead to a simple conclusion: the majority of them came from China. Words of "Manufactured in China" and "Printed in China" are repeatedly seen on the back of the books, in some cases with detailed locations such as "Printed in Foshan City, Guangdong (Province), China."
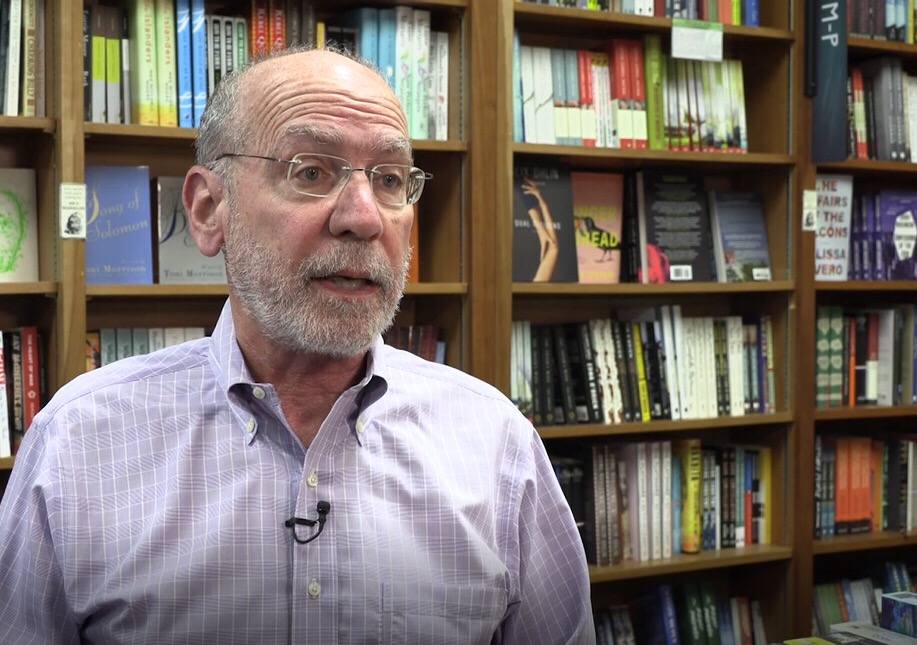
In this video screenshot, Jamie Fiocco, owner of Flyleaf Books, also the president of the American Booksellers Association, which represents some 2,000 independent brick-and-mortar booksellers across the country, speaks during an interview with Xinhua in Chapel Hill in the North Carolina, the United States, Aug. 27, 2019. (Xinhua/Hu Yousong)
While not knowing the overall market share, Fiocco pointed out that some of the children's books made from special materials are exclusively produced in China, such as those called "indestructibles," which are "chew proof, rip proof, nontoxic and 100 percent washable," as stated by publishers.
There has been a trend for printers in China to do four-color printing, a method used to print full-color images, "very well cheaply and quickly," Fiocco told Xinhua earlier. "The best place and the cheapest place and the fastest place tends to be China," Fiocco said.
The video screenshot shows a children's book printed in China at the Flyleaf Books bookstore in Chapel Hill in the North Carolina, the United States, Aug. 27, 2019. (Xinhua)
At a public hearing about the tariff hike on 300 billion U.S. dollars of Chinese products in June, M. Luisa Simpson, vice president for global policy at the Association of American Publishers, said the capacity of U.S. printers has become extremely limited since the 1980s, when the industry began moving out of the country.
Daniel Reynolds, CEO of Workman Publishing, said in his testimony that the majority of the books with colored illustrations are predominately printed in China.
"There is no other viable alternative," Reynolds said. "Any shift to alternative sources, if they're even available, will almost certainly bring a decline in quality."

Workers operate a press to print books at a plant in Gucheng County, north China's Hebei Province, April 8, 2018. (Xinhua/Li Xiaoguo)
"NO MARGIN TO ABSORB"
The U.S. government has recently announced it would impose additional tariffs on 300 billion U.S. dollars worth of Chinese imports, covering clothing, shoes, toys, TVs, cell phones, laptop computers, among other consumer goods.
The extra tariffs, which took effects on Sept. 1 on the first batch of these Chinese imports at 15 percent, have drawn strong backlash from numerous U.S. industry associations, and also prompted Chinese retaliation.
Fiocco said tariffs on black-and-white books, as well as some colored books such cooking books and travel books, are effective from Sept. 1, and tariffs on children's books are delayed until Dec. 15. Partial postponement of the tariffs, however, would not eliminate the impact for independent stores, which usually have fewer resources compared with big bookstore chains.
Photo taken with mobile phone shows a children's book manufactured in China at the Flyleaf Books bookstore in the North Carolina, the United States, Aug. 27, 2019. (Xinhua/Xiong Maoling)
"The tariffs for at least children's books will not come into effect until December 15th with the idea that retailers can stock up. Well, I can assure you that most of the space that we pay rent on is for the front of store. So there's not a lot of storage space," Fiocco said, adding that independent booksellers like herself are often working on short cashflow.
Noting that over a third of their business is done in the holiday season, which runs from late November to the end of December, Fiocco said "we'll buy as many as we can before Dec. 15 and hope that it's enough."
Fiocco said historically, margins for independent bookstores are "very tight," and the most profitable bookstores are usually 8 percent profitable. "If the publishers decide to pass the price along to us, we'll have to do the same (to consumers). So the prices will go up, which no one wants, but that's a reality," she said.
"It's just not possible to absorb an additional 15 percent," she said.
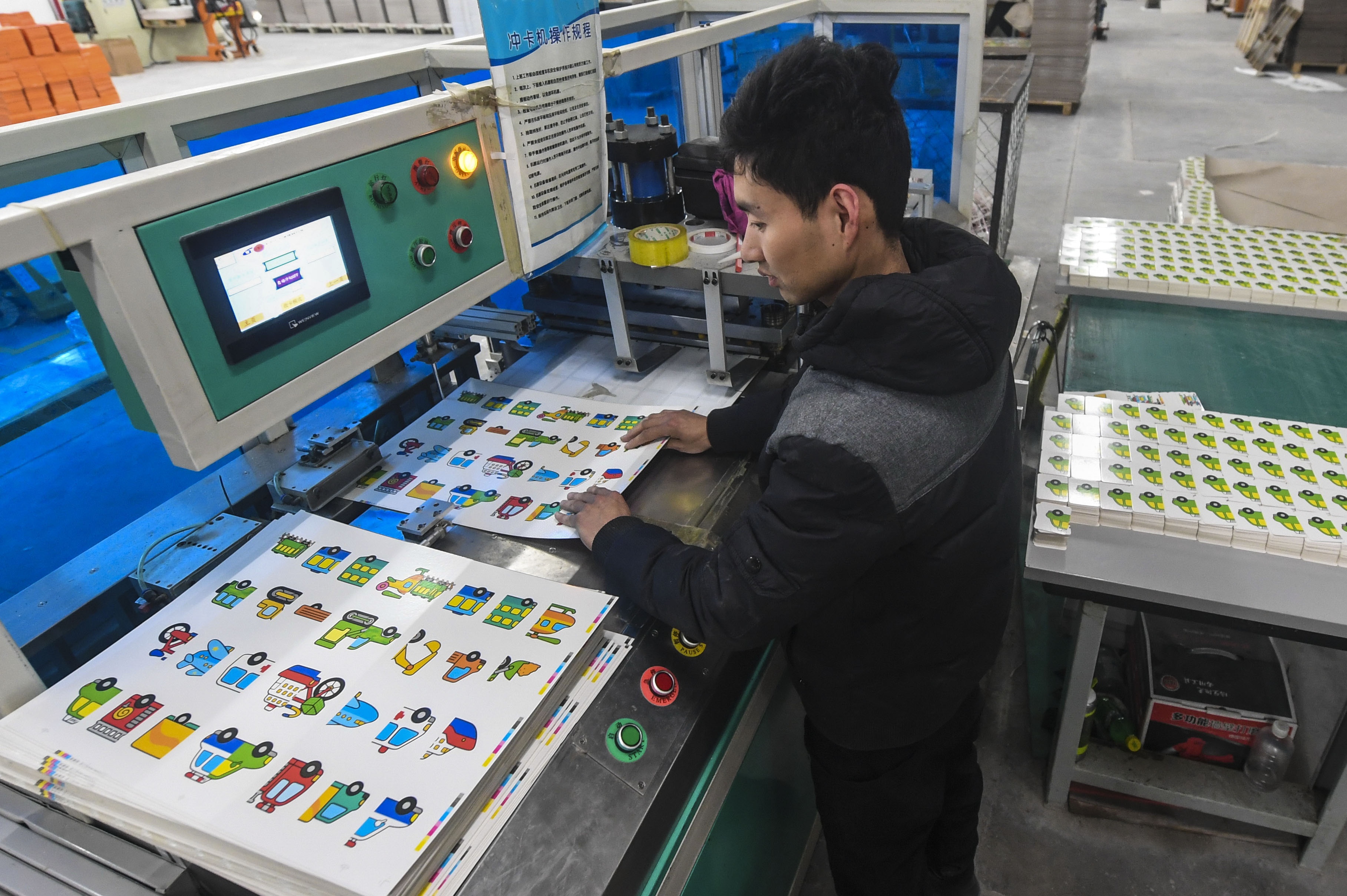

Workers operate a press to print books at a plant in Gucheng County, north China's Hebei Province, April 8, 2018. (Xinhua/Li Xiaoguo)
Others in the industry share Fiocco's worry. Bradley Graham, co-owner of Politics and Prose, a 35-year-old famous bookstore in Washington D.C., told Xinhua that in the wake of the tariffs, chances are publishers will be prompted to raise the price of books, which "would be very hurtful to our sales."
Graham said there's been a net increase in the number of independent bookstores in recent years, in what he calls "a bit of an upturn," following a sharp decline since the 1990s. He attributed the robust growth of independent bookstores in the country to "a commitment by many customers to buy local" and "a leveling off in the popularity of e-books."
"That said, it's still a very challenging business. Our profit margins are still very narrow. The revenues have been going up in many cases, but so have the expenses, particularly payroll and rent," he said. "So there isn't a lot of room for error."
In this video screenshot, Bradley Graham, co-owner of Politics and Prose, a 35-year-old famous bookstore in Washington D.C., speaks during an interview with Xinhua in Washington D.C., the United States, on Aug. 26, 2019. (Xinhua)
TROUBLING PROSPECT FOR CHILDREN
Graham said he is "quite concerned" about the prospect of tariffs on books, which would go against the past U.S. policy that tended not to levy tariffs on books because of their importance to the culture.
"Imposition of tariffs ... would prompt the rise in book prices and that would discourage some people from buying books," he said. "I think that would be damaging to our culture."
After carefully selecting three books for her neighbors' grandchildren, 70-year-old Billie, who only gave her first name, told Xinhua that she is "angry" about the U.S. government's new tariffs on books, particularly children's books.
Billie, a longtime customer of Fiocco's bookstore, said if the prices increase, children would probably have fewer books of their own, and that could deprive them of the opportunities to better develop their reading skills.
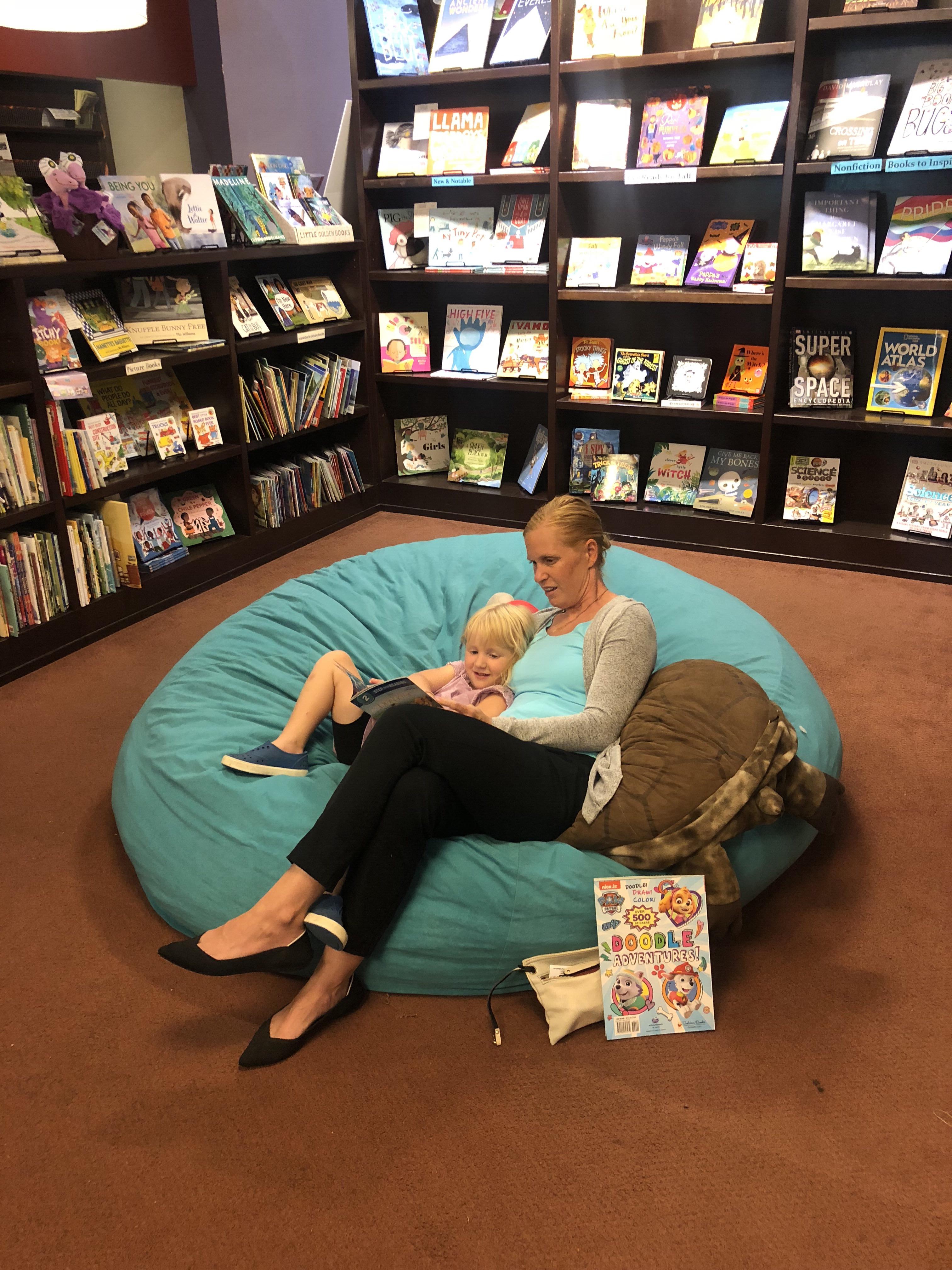

Photo taken with mobile phone shows a woman reading to a girl at the Flyleaf Books bookstore in Chapel Hill in the North Carolina, the United States, Aug. 27, 2019. (Xinhua/Xiong Maoling)
"Our daughter used to almost memorize them because you read them so many times," she said, adding "so it's really good for teaching them how to read."
Echoing Billie, Fiocco said it's disturbing if children aren't allowed access to books as a result of tariffs, adding that this would disproportionately impact low income families.
Fiocco said she works with several organizations that distribute free books to low income families, whose priorities are not reading materials for their children.
"I know for a fact that those budgets will be directly impacted. I don't see how they're going to buy as many books this year if the prices go up," she said.
"It's troubling because you definitely want kids to grow up with books," Fiocco said.
(Video reporters: Hu Yousong, Xiong Maoling; Video editor: Liu Xiaorui)









